Contents
1. Big picture
2. Fork a repository
3. Clone fork repository to local
4. Create a branch to add a new feature or fix issues
5. Commit and Push
6. Create a Pull Request
1. Big picture
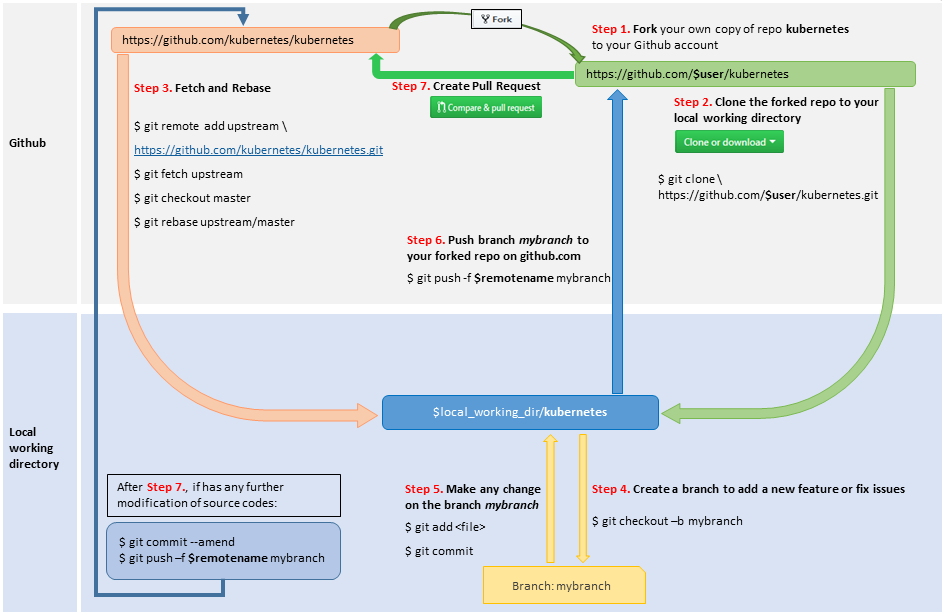
2. Fork a repository
- Goto https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes
- Hit the
Forkbutton to fork your own copy of repo kubernetes to your github account

3. Clone the forked repository to local
Clone the forked repo in above step to your local working directory:
$ git clone https://github.com/$user/kubernetes.git
$ cd kubernetes
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes.git
# Never push to upstream master
$ git remote set-url --push upstream no_push
# Confirm that your remotes make sense:
$ git remote -v
$user = {your github account name}
4. Create a branch to add a new feature or fix issues
Update local working directory:
$ cd kubernetes
$ git fetch upstream
$ git checkout master
$ git rebase upstream/master
Please don’t use git pull instead of git fetch / rebase. git pull does a merge, which leaves merge commits. These make the commit history messy and violate the principle commits.
Create a new branch:
$ git checkout -b mybranch
5. Commit and Push
Commit
Make any change on the branch mybranch then build and test your codes.
Include in what will be committed:
$ git add <file>
Commit your changes:
$ git commit
Enter your commit message to describe the changes. See the tips for a good commit message at here.
Likely you go back and edit/build/test some more then git commit --amend
Push
Push your branch mybranch to your forked repo on github.com.
$ git push -f $remotename mybranch
6. Create a Pull Request
- Go to your fork at https://github.com/$user/kubernetes
- Hit the button
next to branch
mybranch - Flow the following processes to create a new pull request
